How To Set Up Base Stations

Base station (or base radio station) is – according to the International Telecommunication Wedlock's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)[1] – a "land station in the country mobile service."
The term is used in the context of mobile telephony, wireless computer networking and other wireless communications and in land surveying. In surveying, information technology is a GPS receiver at a known position, while in wireless communications it is a transceiver connecting a number of other devices to ane another and/or to a wider area. In mobile telephony, information technology provides the connection between mobile phones and the wider telephone network. In a computer network, information technology is a transceiver acting as a switch for computers in the network, perhaps connecting them to a/another local surface area network and/or the Net. In traditional wireless communications, it can refer to the hub of a dispatch fleet such as a taxi or delivery fleet, the base of a TETRA network as used by government and emergency services or a CB shack.
Land surveying [edit]
In the context of external land surveying, a base station is a GPS receiver at an accurately-known stock-still location which is used to derive correction information for nearby portable GPS receivers. This correction data allows propagation and other effects to be corrected out of the position data obtained by the mobile stations, which gives greatly increased location precision and accuracy over the results obtained past uncorrected GPS receivers.
Computer networking [edit]
In the area of wireless computer networking, a base station is a radio receiver/transmitter that serves every bit the hub of the local wireless network, and may also be the gateway betwixt a wired network and the wireless network. Information technology typically consists of a low-power transmitter and wireless router.
Wireless communications [edit]
In radio communications, a base station is a wireless communications station installed at a fixed location and used to communicate equally part of one of the following:
- a push-to-talk two-mode radio arrangement, or;
- a wireless telephone system such as cellular CDMA or GSM cell site.
- Terrestrial Trunked Radio
Base stations use RF power amplifiers (radio-frequency ability amplifiers) to transmit and receive signals. The near common RF power amplifiers are metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), peculiarly LDMOS (power MOSFET) RF amplifiers.[ii] [3] [iv] RF LDMOS amplifiers replaced RF bipolar transistor amplifiers in almost base stations during the 1990s,[two] leading to the wireless revolution.[five]
Two-way radio [edit]
Professional [edit]
In professional person two-mode radio systems, a base station is used to maintain contact with a dispatch fleet of hand-held or mobile radios, and/or to actuate one-way paging receivers. The base station is one stop of a communications link. The other cease is a movable vehicle-mounted radio or walkie-talkie.[6] Examples of base of operations station uses in two-way radio include the dispatch of tow trucks and taxicabs.
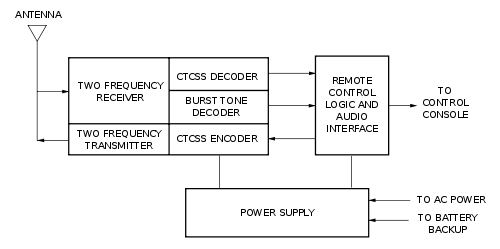
Basic base station elements used in a remote-controlled installation. Selective calling options such equally CTCSS are optional.
Professional person base station radios are frequently 1 aqueduct. In lightly used base stations, a multi-channel unit may exist employed.[7] In heavily used systems, the capability for additional channels, where needed, is achieved by installing an additional base station for each channel. Each base station appears equally a unmarried channel on the dispatch center control panel. In a properly designed dispatch eye with several staff members, this allows each dispatcher to communicate simultaneously, independently of one some other, on a unlike channel as necessary. For example, a taxi visitor dispatch eye may have ane base station on a high-ascent edifice in Boston and another on a different aqueduct in Providence. Each taxi dispatcher could communicate with taxis in either Boston or Providence by selecting the respective base of operations station on his or her panel.[viii]
In dispatching centers it is common for viii or more than radio base stations to be connected to a single dispatching console. Dispatching personnel can tell which channel a message is being received on by a combination of local protocol, unit identifiers, volume settings, and busy indicator lights. A typical panel has two speakers identified equally select and unselect. Audio from a master selected channel is routed to the select speaker and to a headset. Each channel has a busy light which flashes when someone talks on the associated channel.[nine]
Base stations can be local controlled or remote controlled. Local controlled base stations are operated by forepart console controls on the base station cabinet. Remote command base stations can exist operated over tone- or DC-remote circuits. The dispatch point console and remote base station are continued by leased individual line phone circuits, (sometimes called RTO circuitsouthward), a DS-1, or radio links.[ten] The consoles multiplex transmit commands onto remote control circuits. Some system configurations require duplex, or four wire, audio paths from the base station to the panel. Others require just a two-wire or half duplex link.[11]
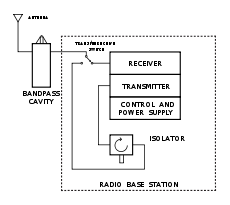
The diagram shows a band-pass filter used to reduce the base station receiver'due south exposure to unwanted signals. Information technology also reduces the transmission of undesired signals. The isolator is a 1-way device which reduces the ease of signals from nearby transmitters going up the antenna line and into the base station transmitter. This prevents the unwanted mixing of signals inside the base of operations station transmitter which tin generate interference.
Interference could exist defined as receiving whatever betoken other than from a radio in your own organisation. To avert interference from users on the same aqueduct, or interference from nearby potent signals on another channel, professional base stations utilize a combination of:[12] [13]
- minimum receiver specifications and filtering.[14] [15] [16]
- analysis of other frequencies in use nearby.
- in the US, coordination of shared frequencies by coordinating agencies.[17]
- locating equipment so that terrain blocks interfering signals.
- employ of directional antennas to reduce unwanted signals.
Base stations are sometimes chosen control or stock-still stations in US Federal Communications Committee licensing. These terms are defined in regulations inside Part 90 of the commissions regulations. In US licensing jargon, types of base of operations stations include:
- A stock-still station is a base station used in a organization intended just to communicate with other base stations. A fixed station can too be radio link used to operate a distant base of operations station by remote control. (No mobile or hand-held radios are involved in the arrangement.)
- A command station is a base station used in a system with a repeater where the base of operations station is used to communicate through the repeater.
- A temporary base of operations is a base station used in one location for less than a year.
- A repeater is a type of base station that extends the range of hand-held and mobile radios.
Amateur and hobbyist employ [edit]
In amateur radio, a base station also communicates with mobile rigs only for hobby or family communications. Amateur systems sometimes serve every bit dispatch radio systems during disasters, search and rescue mobilizations, or other emergencies.
An Australian UHF CB base of operations station is another example of role of a system used for hobby or family communications.
Wireless telephone [edit]
Wireless telephone differ from ii-way radios in that:
- wireless telephones are circuit switched: the communications paths are set up by dialing at the start of a phone call and the path remains in place until one of the callers hangs upwardly.
- wireless telephones communicate with other telephones usually over the public switched telephone network.
A wireless telephone base of operations station communicates with a mobile or hand-held phone. For example, in a wireless phone system, the signals from one or more mobile telephones in an area are received at a nearby base station, which and so connects the phone call to the land-line network. Other equipment is involved depending on the system architecture. Mobile phone provider networks, such as European GSM networks, may involve carrier, microwave radio, and switching facilities to connect the telephone call. In the case of a portable phone such as a United states of america cordless phone, the connection is directly continued to a wired country line.
Emissions issues [edit]

A jail cell tower near Thicketty, South Carolina.
While low levels of radio-frequency power are usually considered to take negligible effects on health, national and local regulations restrict the blueprint of base stations to limit exposure to electromagnetic fields. Technical measures to limit exposure include restricting the radio frequency ability emitted past the station, elevating the antenna to a higher place ground level, changes to the antenna design, and barriers to foot or road traffic. For typical base stations, significant electromagnetic energy is only emitted at the antenna, not along the length of the antenna tower.[eighteen]
Because mobile phones and their base stations are two-style radios, they produce radio-frequency (RF) radiation in gild to communicate, exposing people near them to RF radiation giving concerns about mobile phone radiation and health. Hand-held mobile telephones are relatively low power so the RF radiation exposures from them are more often than not depression.
The World Wellness Organization has concluded that "there is no convincing scientific testify that the weak RF signals from base stations and wireless networks cause adverse health effects."[19]
The consensus of the scientific community is that the power from these mobile phone base station antennas is too low to produce health hazards equally long as people are kept away from directly access to the antennas. However, electric current international exposure guidelines (ICNIRP) are based largely on the thermal furnishings of base station emissions, NOT considering the not-thermal effects harmless.
Emergency ability [edit]
Fuel prison cell backup ability systems are added to critical base of operations stations or cell sites to provide emergency power.[twenty] [21]
Media [edit]
-

-

-
Close-up of a base station antenna in Mexico City, Mexico. There are three antennas: each serves a 120-degree segment of the horizon. The microwave dish links the site with the phone network.
-
A professional rack-mount iDEN Base of operations Radio at a Cell Site.
-

136–174 MHz US professional person base of operations station antenna examples.
-

Cellular network base station in Yekaterinburg
See also [edit]
- Base of operations transceiver station
- Mobile switching center
- Macrocell
- Microcell
- Picocell
- Femtocell
- Access point base of operations station
- Jail cell site
- Cellular repeater
- Mobile phone
- Mobile telephone radiation and health
- Portable phone
- Betoken strength
- Audio level compression
- OpenBTS
- Bandstacked
References [edit]
- ^ ITU Radio Regulations, Department 4. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.71, definition: "base station / base of operations radio station"
- ^ a b Baliga, Bantval Jayant (2005). Silicon RF Power MOSFETS. Earth Scientific. p. 71. ISBN9789812561213.
- ^ Asif, Saad (2018). 5G Mobile Communications: Concepts and Technologies. CRC Printing. p. 134. ISBN9780429881343.
- ^ "Mobile & Wideband Comms". ST Microsystem electronics . Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ Baliga, Bantval Jayant (2005). Silicon RF Power MOSFETS. World Scientific. ISBN9789812561213.
- ^ "Evaluating Regional Alternatives: Systems Design Considerations," Planning Emergency Medical Communications: Volume ii, Local/Regional Level Planning Guide, (Washington, D.C.: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, US Department of Transportation, 1995) pp. 39–43.
- ^ Block diagram is from: "Figure 2: Two Channel VHF Base Station," Planning Emergency Medical Communications: Volume two, Local/Regional Level Planning Guide, (Washington, D.C.: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, US Department of Transportation, 1995) pp. 42.
- ^ Base stations in land mobile systems are often located at remote sites such as hilltops or water towers. Some are controlled from two or more locations. For example, a base of operations station used to communicate with taxis may be continued to remote control consoles at both a taxi company office and an answering service for afterwards-hours calls. The taxi visitor and answering service may be miles apart. Unmarried channel base stations reduce confusion past eliminating the possibility that the incorrect channel may be selected.
- ^ To read more than near multi-channel consoles, look at the service manual for a relatively simple panel: 8-Channel Remote Console, 120, 220, 240 5 AC or 12 Five DC T16167 AM or BM, 68-81021E80, (Schaumburg, Illinois: Motorola, Inc. 1980.) This is a relatively elementary analog console compared to large, enterprise-level Centracom-series units.
- ^ The term RTO circuit is legacy jargon and comes from Bong Organisation billing terminology. RTO circuits refer to analog radio remote control and radio circulate leased phone circuits.
- ^ For a brief word of remote controlled base stations, come across: "Evaluating Regional Alternatives: Systems Design Considerations," Planning Emergency Medical Communications: Volume 2, Local/Regional Level Planning Guide, (Washington, D.C.: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, U.s. Section of Transportation, 1995) pp. 39–41. Tone remote controls are described in this section.
- ^ Cake diagram is from: "Effigy 8: Bandpass Cavity/Isolator Location," Planning Emergency Medical Communications: Book ii, Local/Regional Level Planning Guide, (Washington, D.C.: National Highway Traffic Safety Assistants, United states of america Section of Transportation, 1995) pp. 57.
- ^ Bulleted items condensed from, "European monetary system Communications," "Arrangement Coordination," and "Site Applied science," in Planning Emergency Medical Communications: Volume ii, Local/Regional Level Planning Guide, (Washington, D.C.: National Highway Traffic Prophylactic Administration, U.s.a. Department of Transportation, 1995) pp. ten–19, 55–58.
- ^ For an example of receiver specifications, see, "Table ix-3," 800 MHz Trunked Radio Request for Proposals: Public Safety Projects Part, (Oklahoma Metropolis, Oklahoma: Oklahoma City Municipal Facilities Authority, 2000, pp. 181.
- ^ A list of types of filtering used to forestall interference betwixt equipment at the same site is included in "half dozen.ii.four Electromagnetic Compatibility Studies," 800 MHz Trunked Radio Request for Proposals: Public Safety Projects Office, (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma: Oklahoma City Municipal Facilities Dominance, 2000, pp. 119.
- ^ More detail of interference reduction equipment is provided in, "9.1.ii Base Station/Mobile Relay, 800 MHz," 800 MHz Trunked Radio Asking for Proposals: Public Prophylactic Projects Office, (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma: Oklahoma Urban center Municipal Facilities Authority, 2000, pp. 165–168.
- ^ For case, US federal authorities systems are coordinated and licensed by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration. Business organisation/Industrial Pool licenses are coordinated by the Personal Communications Industry Clan (PCIA) and licensed by the Federal Communications Committee.
- ^ Warren PM (2006). IEEE C95.i-2005 "IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, iii kHz to 300 GHz" Sources: US Department of Health; The World Health Organization. IEEE.
- ^ "Electromagnetic fields and public health: Base stations and wireless technologies". World Wellness Organization. Archived from the original on January nineteen, 2022. Retrieved 2014-09-08 . .
- ^ Ballard fuel cells to power telecom backup ability units for motorola Archived 2022-07-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ India telecoms to get fuel cell power Archived November 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
External links [edit]
- Occupational Safety and Health Admin. Non-Ionizing Radiation Exposure Guidelines.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Base_station



0 Response to "How To Set Up Base Stations"
Post a Comment